-
WordPress
Once you have your WordPress site set up, it is time to start working on the design of your site. This can be an intimidating task for those without any web design experience. Luckily, WordPress has built-in themes to help you customize the design of your site. A WordPress theme is a group of files containing style sheets, graphics, and code that dictates the appearance of your site.
While there are thousands of free themes, there are premium themes that have a cost attached to them. Free themes typically have fewer features and fewer in-depth customization options than premium themes. The free ones are also updated less frequently than the premium ones. Premium themes are typically a one-time purchase with prices ranging from $10 up to $200, with most costing around $59.
In WordPress, a child theme is a theme that inherits the functions, features, and style of another theme, called the parent theme. The child theme can then be customized without making any changes to the parent theme. The main advantage to using a child theme is that it allows you to safely update the parent theme without losing any of the customizations that are made in the child theme. To locate themes in WordPress, click on Appearance in the menu from the Dashboard and then click on Themes. From here click on Add New, and you will have access to thousands of themes.
To locate themes in WordPress, click on Appearance in the menu from the Dashboard and then click on Themes. From here click on Add New, and you will have access to thousands of themes.

If you click on Feature Filter, you can filter your theme searches by subject, layout, or by features that best fit the needs of your website. Once you have chosen a theme you like, you can install it by clicking on the install button.
Then go back to the Themes page and click Activate to make that theme the theme of your site.
Themes can be customized in WordPress by clicking on the Customize button.

From here you can easily make changes to your theme by navigating the customization menu on the left of the screen.
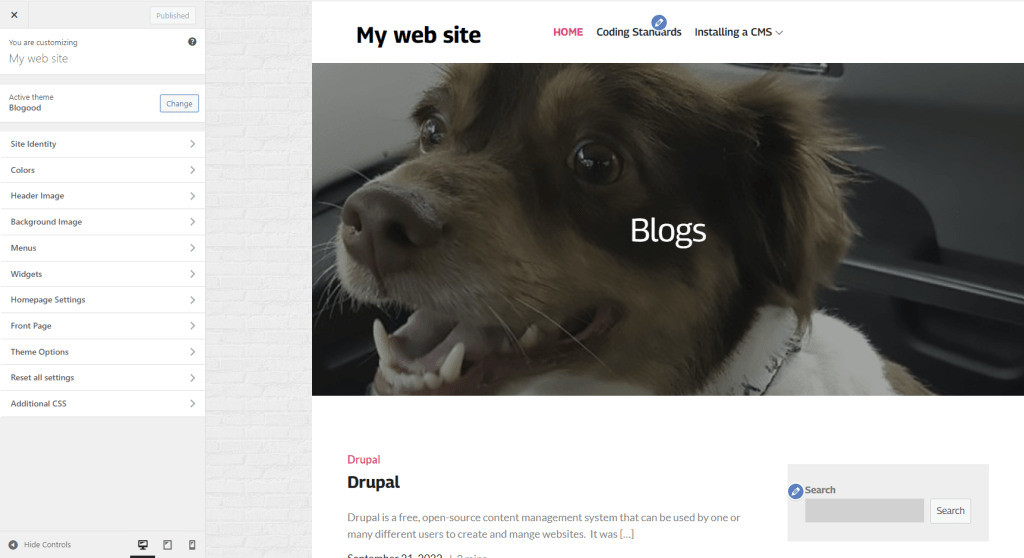
If you want to make changes to your theme, but the option you are looking for isn’t in the menu, you can click on the Additional CSS button at the bottom of the menu to make changes manually by writing CSS code.
-
Drupal
Drupal
Drupal is a free, open-source content management system that can be used by one or many different users to create and mange websites. It was designed to be easy to use so that even people lacking technical skills can create their own websites. Drupal uses PHP and is ready to use as soon as it is downloaded.
Before installing Drupal, first, you need to make sure that you meet all the system requirements so that the software will work. First, visit drupal.org/docs, here you can find links to all the information you could ever need about Drupal. From here, click on the System Requirements link to go a list of the requirements for Drupal.
After making sure that you meet all the requirements, you need to make sure that you have a new, empty database. How you create this database will vairy depending on your database software. I used XAMPP and created a local database using phpMyAdmin. Make sure that your database has a name, address, username, and password so that Drupal can access it.
Now you will need to download Drupal. To do this, visit druapl.org/download. Drupal recommends using something called composer to install and run Drupal, but I did it without using composer and had no problems downloading it. What I did is click on the Download Drupal | zip link, to download the Drupal.zip file.
After that, I extracted all the files, and copied the unzipped folder into my htdocs folder so that it could be accessed thru my local host. The steps you take may be different if you are using different software or if you are not using a local host. To begin the setup process, I typed localhost:8080/drupal into my browser’s URL bar. I then entered all the necessary information and created an account. After completing the setup process, I was taken to the Drupal dashboard.
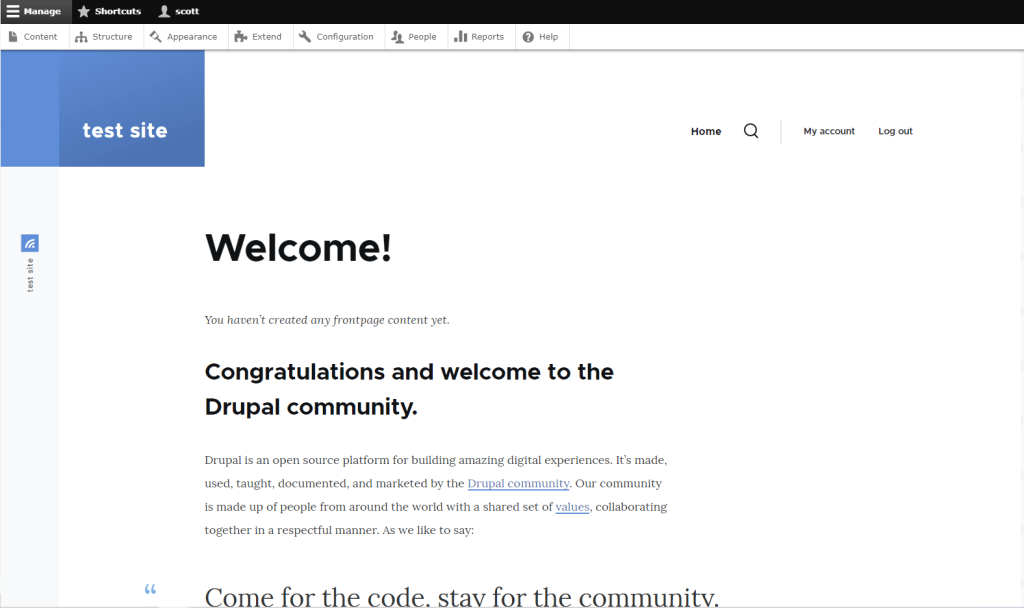
From here I was able to create a site. There are plenty of resources to help you learn how to use Drupal I used Linked-In Learning, but the other ones I looked at seemed just as helpful. I didn’t find Drupal too difficult to use once I spent some time with it and see how it would be helpful in making an actual website.
-
Installing a CMS
A content management system (CMS) is a computer program used to create and modify digital content. There are many different CMSs such as WordPress, Drupal, Squarespace, and Blogger. I chose to install Expression Engine. I chose this CMS because I was curious as to why it was so popular.
To install Expression Engine first, you go to expressionengine.com, scroll down the page, then click on the View the Docs link.
From here you will want to click on Installation & Updates, then click on System Requirements. Here you will find a list of software that is required to install and use the CMS.

After making sure that your machine meets all the requirements, you will need an empty database. Creating an empty database varies depending on what software you have or what host you are using. I used XAMPP and created the database locally. You need to make sure that the database has a name, server address, username, and password.
Next, download and unzip the latest release of Expression Engine. To do this go back to the home page and click on the “Free Download” button near the top of the page. Annoyingly, this takes you further down on the page where you click on a second “Free Download” button that downloads the files.
From here, I copied the unzipped folder into the htdocs folder located in the xampp folder. This step may be different if you are using different software or a different host. Then I accessed the installation file in my web browser by typing localhost:8080/expressionengin/admin.php. I then entered the database information and created an account which directed me to the dashboard.
-
Coding Standards
Coding standards (also known as coding conventions) are guidelines for programming languages that dictate methods, practices, and styles for programs written in a specific programming language. Coding standards cover include things like naming conventions, indentation, file organization, programming practices and principles, etc.
Coding standards are used to ensure that all developers working for an organization or on a project follow the same structure and guidelines. This way all code involved in the project can be understood and maintained with ease by everyone involved, not just the developer who wrote the code. The use of standards also enables developers to reuse code from one project to another.
Using coding standards can also improve security. Inconsistencies, bugs, and logical errors can cause vulnerabilities in the software. Most of these problems are caused by poor coding practices. With clean well written code, it is also easier to find and fix any errors that may occur.
Even though most organizations have their own specific coding standards or style guides, some fall back on the World Wide Web Consortium’s (W3C) guidelines. W3C is an international community where people from all around the world work together to develop standards. Both Google and WordPress recommend that developers run their HTML code through the W3C HTML validator. Despite the fact that the use of the validator is recommended, passing validation does not necessarily mean that the code is up to the standards of any specific organization. The validator will catch many errors but there is no substitute for reviewing your code manually.
Coding standards may vary depending on the organization. For example, Google’s coding standards dictate that indentation is to be done with 2 spaces instead of tabs:
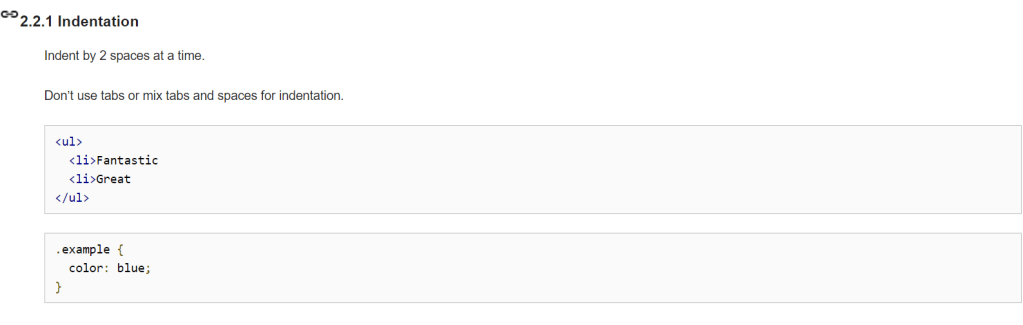
where WordPress coding standards ask that tabs be used for all indentation.

Another example of differences between organizations is that WordPress wants its developers to close all self-closing tags with a forward slash that has a space before it:

But AB Tech’s guidelines ask that similar elements not be closed.
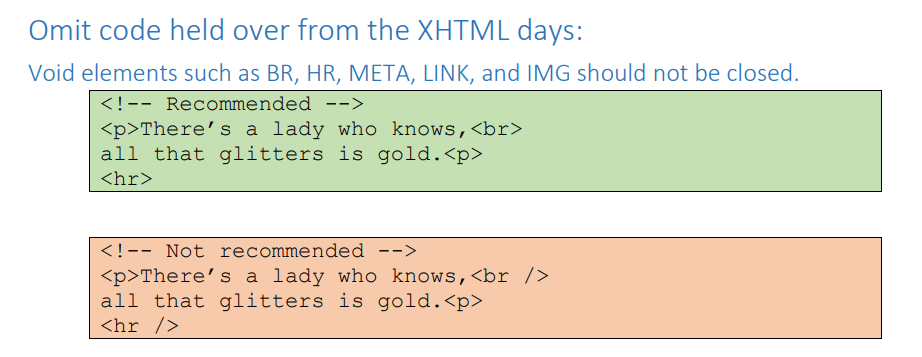
Since there are differences between organizations, it is important to familiarize yourself with the standards of the organization you are working for.
While coding standards are not necessary for a website or program to run, I still believe that they should be used. They make writing and maintaining the code easier, and make things more secure by removing vulnerabilities.
-
Hello World!
Welcome to WordPress! This is your first post. Edit or delete it to take the first step in your blogging journey.
-
Subscribe
Subscribed
Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.